5.1 Simulating Allotetraploid Data
The hespresso package provides functions to simulate artificial read counts for allotetraploid and allohexaploid species. By default, the simulation generates read counts for an allotetraploid with 10,000 homeologs across two conditions, each with three biological replicates. The mean and dispersion parameters are estimated from real RNA-Seq data from an allotetraploid Cardamine flexuosa dataset (Akiyama et al. 2021).
To generate a simulated dataset with default options, run as follows.
## # 2 subgenome sets (A, B)
## # 10000 homeolog tuples
## ---------------------
## Experiment Design:
## group replicate
## 1 group_1 1
## 2 group_1 2
## 3 group_1 3
## 4 group_2 1
## 5 group_2 2
## 6 group_2 3
## ---------------------
## > subgenome: A
## group_1__1 group_1__2 group_1__3 group_2__1 group_2__2 group_2__3
## gene_1 27 22 16 14 14 22
## gene_2 278 4 12 87 113 93
## gene_3 614 316 433 437 228 631
## gene_4 360 341 311 359 237 411
## gene_5 138 42 214 150 189 165
## gene_6 1028 1063 1171 383 385 342
## +++++++++++++++++++++
## > subgenome: B
## group_1__1 group_1__2 group_1__3 group_2__1 group_2__2 group_2__3
## gene_1 9 21 11 21 19 21
## gene_2 124 107 123 218 187 200
## gene_3 162 149 206 180 235 259
## gene_4 373 329 384 353 269 374
## gene_5 63 45 69 75 49 43
## gene_6 101 93 102 67 98 83
## ---------------------Options can be flexibly customized by users. For example, to simulate data with 1,000 homeologs and 5 replicates per condition, run as follows.
## # 2 subgenome sets (A, B)
## # 1000 homeolog tuples
## ---------------------
## Experiment Design:
## group replicate
## 1 group_1 1
## 2 group_1 2
## 3 group_1 3
## 4 group_1 4
## 5 group_1 5
## 6 group_2 1
## 7 group_2 2
## 8 group_2 3
## 9 group_2 4
## 10 group_2 5
## ---------------------
## > subgenome: A
## group_1__1 group_1__2 group_1__3 group_1__4 group_1__5 group_2__1 group_2__2 group_2__3 group_2__4 group_2__5
## gene_1 59 58 58 51 47 70 43 71 53 45
## gene_2 8 2 5 36 13 6 9 6 7 6
## gene_3 4 4 4 4 9 0 0 1 8 0
## gene_4 27 34 34 28 18 8 6 10 18 15
## gene_5 52 43 32 54 37 31 10 5 22 10
## gene_6 1273 1749 1696 2733 1867 1506 1748 1757 2009 1948
## +++++++++++++++++++++
## > subgenome: B
## group_1__1 group_1__2 group_1__3 group_1__4 group_1__5 group_2__1 group_2__2 group_2__3 group_2__4 group_2__5
## gene_1 12 3 36 0 7 23 21 19 26 13
## gene_2 6 3 5 2 7 0 0 0 0 0
## gene_3 6 7 9 10 4 8 8 12 8 8
## gene_4 33 12 2 0 1 7 5 11 2 8
## gene_5 202 136 178 156 189 188 167 163 167 153
## gene_6 793 842 918 800 937 989 1112 845 945 992
## ---------------------Simulated read counts are generated from a negative binomial (NB) distribution.
The mean and dispersion values used for each homeolog are stored in the object returned by sim_homeolog_counts().
The get_sim_params() function can be used to retrieve these parameters.
For example, to get means used for sampling read counts, run as follows.
## [1] "group_1" "group_2"## A B
## gene_1 56.491374 17.328355
## gene_2 8.006597 4.818938
## gene_3 5.944184 6.766986
## gene_4 28.174125 7.362780
## gene_5 44.853340 166.388422
## gene_6 1902.944015 899.045310The output is a list of data frames, one per condition, with columns representing individual subgenomes. These ground-truth mean values can be used to calculate true homeolog expression ratios for each condition. Users can then define homeologs that show significant changes in expression ratios between conditions.
Alternatively, the def_sigShift() function can automatically
define homeologs with significant shifts without manual calculations.
For example, to identify homeologs with a maximum absolute ratio difference (Dmax) greater than 0.2
or a maximum odds ratio (ORmax) exceeding 2.0, use the following code.
x <- sim_homeolog_counts()
is_sig <- def_sigShift(x, Dmax = 0.2, ORmax = 2, operator = "OR")
table(is_sig)## is_sig
## FALSE TRUE
## 9260 740The output shows the number of homeologs meeting these thresholds.
To visualize the distribution of expression ratios across conditions,
use the plot_HER_distr() function.
This returns a list of histograms, one per condition,
with ratios calculated by default for the first subgenome (base = 1).
Since the simulated dataset contains two groups,
the plot_HER_distr() function returns two histograms.
## [1] "group_1" "group_2"To display the distributions for each group, run as follows.
library(ggplot2)
library(gridExtra)
grid.arrange(distr_plots[["group_1"]] + ggtitle("group_1"),
distr_plots[["group_2"]] + ggtitle("group_2"),
ncol = 2)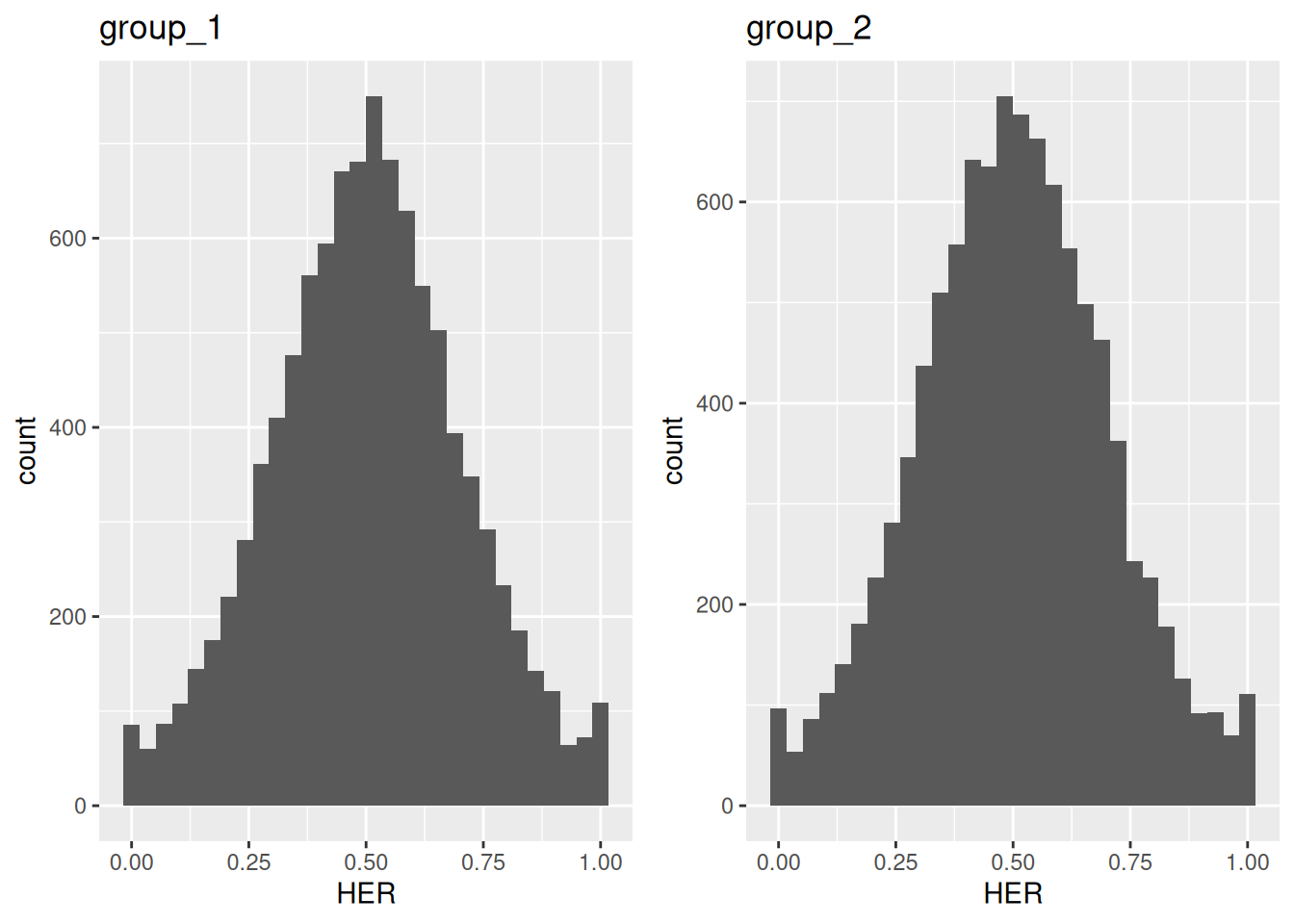
Figure 5.1: Distribution of homeolog expression ratios in two simulated groups.
To compare expression ratios between groups, use the plot_HER() function,
which by default plots ratios for the first subgenome in a scatter plot.
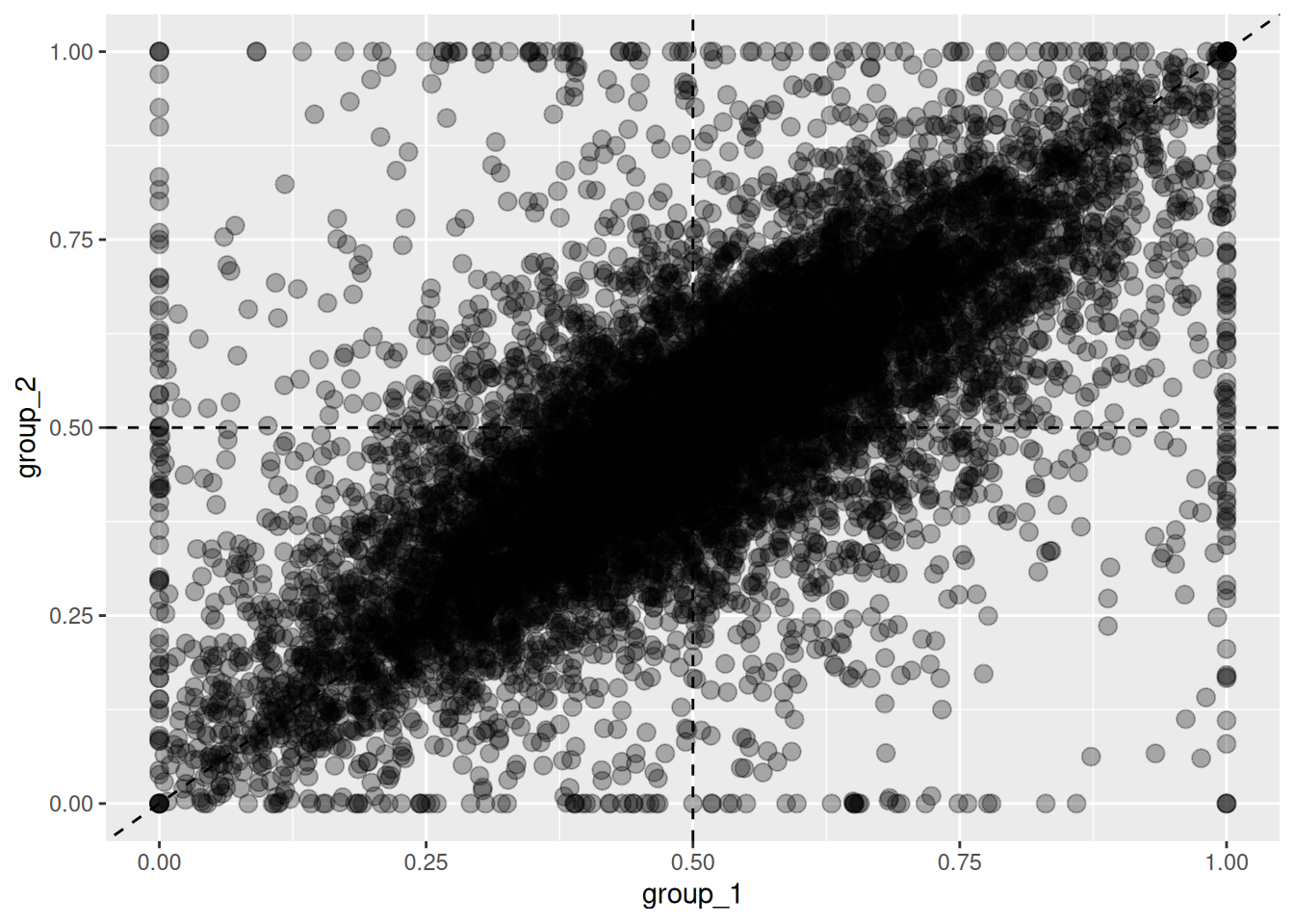
Figure 5.2: Changes in homeolog expression ratios between two groups. Each point represents the expression ratio in group 1 (x-axis) and group 2 (y-axis).
If the dataset was generated using sim_homeolog_counts(),
ground-truth significant shifts can be highlighted as follows using the def_sigShift() function.
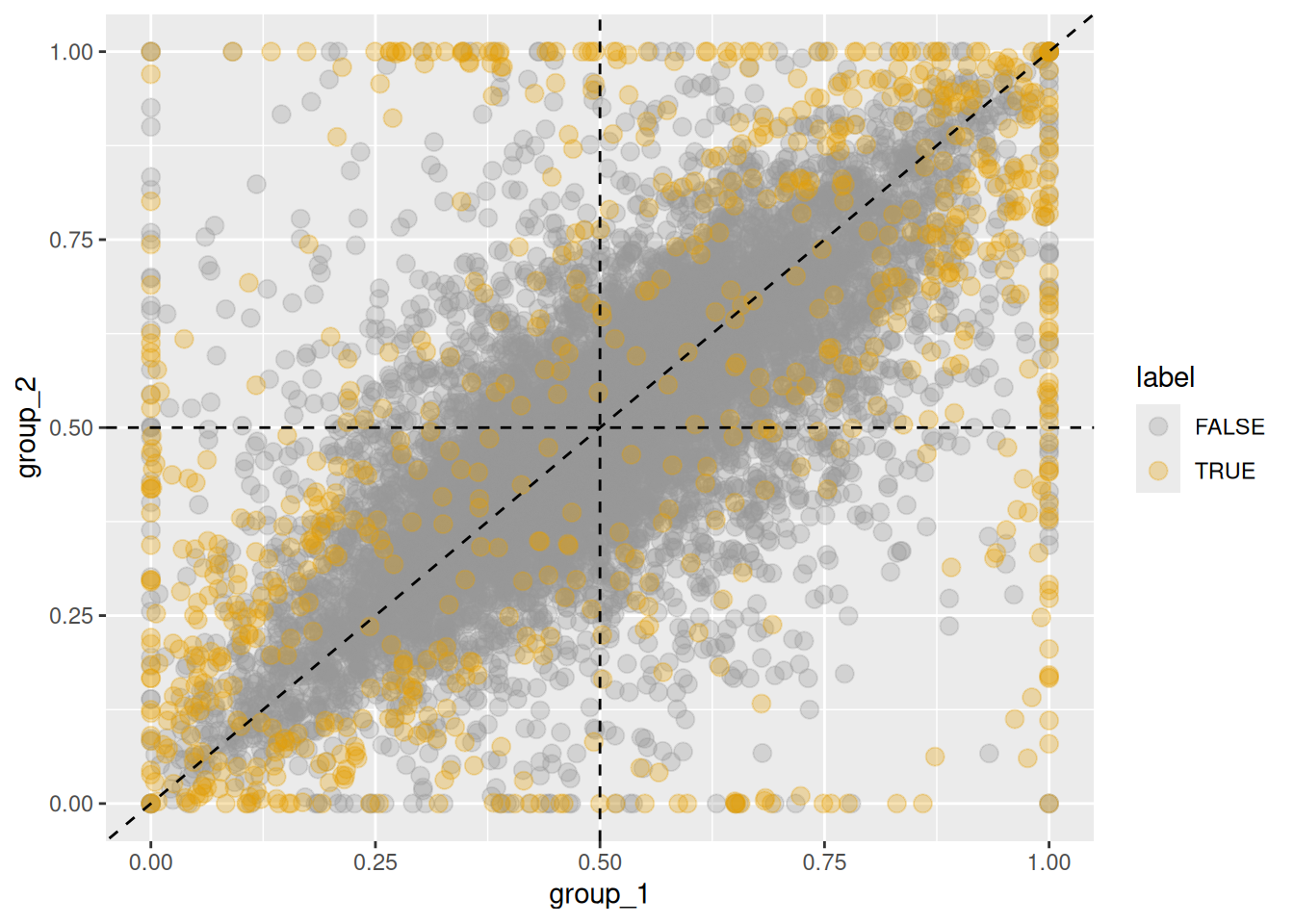
Figure 5.3: Changes in homeolog expression ratios between two groups. Orange points indicate homeologs with significant changes in expression ratios, while gray points represent those without significant changes.